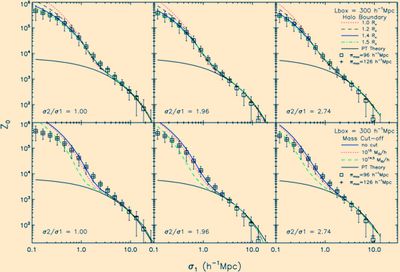
Fig.1 Z0 of the box300 simulation (z = 0) with predictions from the halo model and Eulerian PT. Symbols are measurements of simulations in real spacewith different πmax. The upper row of plots shows the effects of adjusting the halo boundary radius in units of Rv but without a cut-off to the halo mass function,while the bottom row demonstrates the consequence of cutting the high-mass tails of the mass function with the halo boundary fixed to Rv. Dr. MENG Kelai et al. ,Purple Mountain Observatory, Chinese Academy of Science, have proposed a redshift-distortion-free correlation function at third order in the non-linear regime for characterzing galaxy clustering properties. The zeroth-order component of the cosine expansion of the projected three-point correlation function is proposed for the clustering analysis of cosmic large-scale structure. These functions are third-order statistics but can be measured similarly to the projected two-point correlations. Numerical experiments with N-body simulations indicate that the advocated statistics are redshift distortion free within 10 per cent in the non-linear regime on scales of ∼0.2–10 h−1Mpc.In addition, the maximal integration scale πmax parallel to the LOS during estimation ought to be greater than ∼ 120 h−1Mpc. A serious concern is that shot noise could ruin the estimation in the strongly non-linear regime if the number density of points in a sample is too low. This requirement for a robust Z0 measurement is tighter than that for the projected 2PCF, but still weaker than the normal projected 3PCF, since Z0 is an integral of the former. As we expected, the halo model provides satisfactory predictionto the dark matter Z0 of simulations within ∼10 per cent, if theclassical Sheth–Tormen mass functions are used. Our computationindicates that extending the halo boundary is enough to yield a good fit to simulations, while a hard cut-off to mass function is notas effective as previous works claimed. Substituting new functionsof the halo mass distribution and halo biasing in high precisiondoes not lead to significantly better agreement with simulations.Since the angular dependence in the projected 3PCF and the normal3PCF is smeared out in Z0, we conjecture that using an anisotropichalo profile will probably not improve accuracy significantly. Asignificant bias of the Z0 predicted by the halo model comparedto simulations emerges in the weakly non-linear regime, where thehalo models reduce to second-order PT; the latter is already knownto be poor in predicting the dark matter 3PCF. A more precisebispectrum from higher order perturbation theories may offer a wayto increase precision (e.g. Valageas 2008; Sefusatti 2009; Bartoloet al. 2010).The agreement between halo model and actual measurementlays the ground for using these functions to perform joint analyses with the projected two-point correlation functions, exploring galaxy clustering properties in the framework of the halo model and relevant extensions.The work by MENG Kelai (corresponding author), PAN Jun, István Szapudi, FENG Longlong, accepted by Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, has been published online (http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18247.x/abstract;jsessionid=F29DA822621BA8ADCF8EDE0875496487.d02t01). |




