The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (KHI), driven by a shear of the flow velocity, has been observed in various astrophysical environments. Shear-flow-driven instability can play an important role in energy transfer processes in the solar coronal plasma. Dr. Li Feng and her collaborators for the first time present the observation of a kink-like oscillation of a streamer that is probably caused by the streaming kink-mode Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (KHI). The wave-like behavior of the streamer was observed by the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph Experiment C2 and C3 on board the SOlar and Heliospheric Observatory. The free energy driving the instability is supplied by the sheared flow and sheared magnetic field across the streamer plane. The authors also estimated the plasma properties of the local environment of the streamer from the phase speed and instability threshold criteria. This work was published on Astrophysical Journal on September 10 2013 (774, 141), and was supported by MSTC Program 2011CB811402, NSFC under grants 11003047, 11233008, 11273065 and German DLR contract 50 OC 1301. 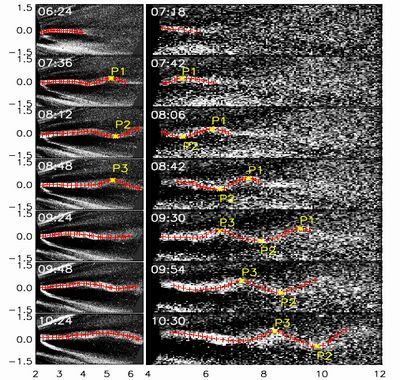 By with FENG li Some selections of the traced streamer in oscillation by LASCO C2 and C3 coronagraph images. The yellow asterisks mark the crests and trough along the streamer.
|




